
Welcome to DISCo: Digital and Sustainable Construction. We conduct cutting-edge interdisciplinary research to shape the future of construction. Our focus is on attracting talented researchers and fostering collaboration between industry and academia. We aim to develop integrated digitalization frameworks to enhance sustainability throughout construction project lifecycles.
In today’s landscape of construction business, digitalization and sustainability are the two most influencing market trends. Each has sparked a slew of research on how it will change engineering, management, and society. However, the interplay of these trends is still mainly unexplored.

Digitalization
Construction projects are evolving towards increased complexity and intricacy, marked by heightened risks, uncertainties, and substantial capital investments. The multitude of processes managed by diverse professional entities necessitates meticulous planning and execution.
Digitalization emerges as a key enabler, offering integration opportunities throughout the construction value chain. This paves the way for achieving sustainability in the construction sector. Considering technological risks and path dependencies, we advocate for innovative and sustainable approaches to integrate both soft and hard digital systems into Construction Engineering and Management (CEM).
In the realm of digitalization in construction, our research prominently focuses on the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as a disruptive technology in CEM. The adoption of AI holds the potential to expedite decision-making, enhance efficiency, and mimic human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, and self-correction, thereby contributing to the advancement of the construction industry.
AI-driven systems exhibit a progressive nature, continuously learning from unbiased facts. With a robust data structure, AI possesses the capability to autonomously facilitate real-time decision-making, revolutionizing the governance of construction processes. Our research in applying AI to the construction sector spans various domains, including but not limited to:
- Automated Planning and Pattern Recognition: Utilizing model-based intelligent behavior through process mining.
- Advanced Machine Learning and Process Optimization Algorithms: Developed for decision support and problem-solving, akin to an expert system.
- Predictive Cost Overrun Models
- Structural Damage Assessment
- Waste Generation and Energy Management
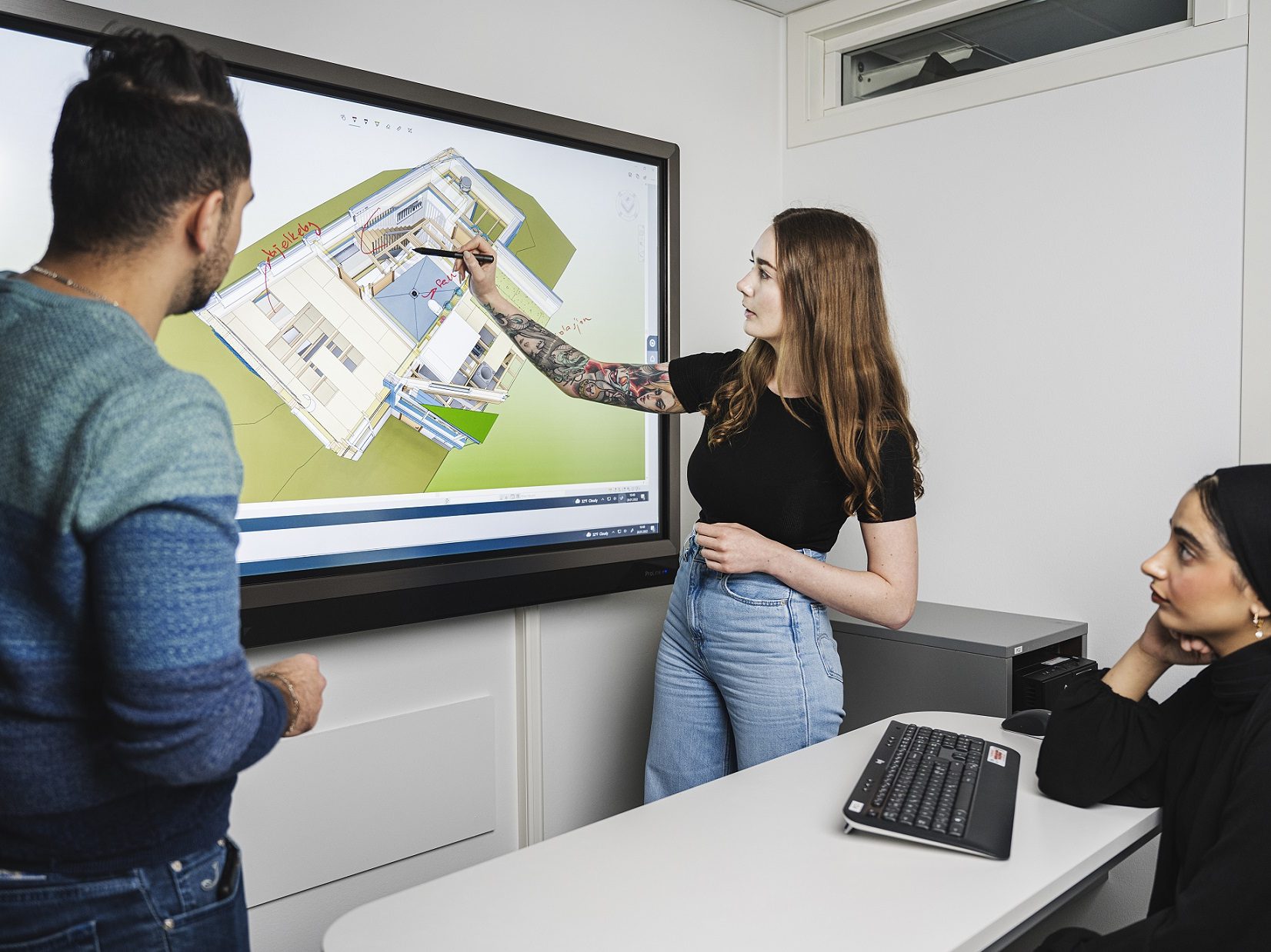


Exploring beyond AI, we passionately delve into sustainable digital transformation within construction management and processes. Presently, building information modeling (BIM) stands at the forefront of digitalization in the construction sector. Harnessing the capabilities of AI, our goal is to unlock the full potential of BIM for generative design, planning, construction, structural health monitoring (SHM), and efficient management procedures.
In our pursuit, we scrutinize the manifold applications of BIM across all construction phases. Moreover, we explore cutting-edge integration of BIM with other digitalization practices, paving the way for the seamless automation of construction processes. Our digital solutions encompass an array of advanced technologies, such as digital twins, sensor management systems, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), 3D scanning, 3D printing, drones, and robotics, among others.
Sustainability
Sustainability is the primary moral and economic imperative of the 21st century. It is one of the most important sources of both opportunities and risks for businesses “
Mervyn King, former Bank of England governor.
Aligned with global trends, our research is dedicated to advancing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), focusing on the three pillars of economic, environmental, and social sustainability.
Recognizing the profound impact of construction projects on social communities, we acknowledge the industry’s position as one of the most resource- and energy-intensive sectors. With immense potential to bolster all facets of sustainability, achieving long-lasting sustainability is a complex undertaking. It necessitates the synthesis and interpretation of vast amounts of information by decision-makers, given the interconnected nature of the three sustainability pillars.


We leverage the opportunities presented by digitalization to accelerate sustainability practices in Construction and Engineering Management (CEM). In this context, we are committed to developing strategies that encompass:
- Systematic Identification and Advancement: Uncovering and advancing sustainable construction methods and innovations systematically.
- BIM for Comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Harnessing Building Information Modeling (BIM) for high-quality environmental, economic, and social Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) practices.
- Integrated Monitoring and Innovative Decision-Making: Pioneering new integrated monitoring techniques and innovative decision-making processes to facilitate circular transformation throughout the construction value chain.
- Lean Construction, Automation, and Modularization (LAM): Effectively implementing Lean Construction, Automation, and Modularization (LAM) for streamlined and efficient processes.
- Decoupling Energy Consumption and Resource Use: Decoupling energy consumption, resource use, and growth in the construction sector through the integration of renewable energies and efficiency measures into design and processes.
- Sustainable Development Compliance: Ensuring the sustainable development of construction approaches to comply with evolving regulations and taxonomies.
Knowledge application
The dissemination of knowledge pertaining to the advancement of the construction industry encompasses a diverse audience, ranging from the international scientific community to building professionals, users, and authorities.
Furthermore, the research activities of the group are intricately connected to an educational context. Several courses and specializations within our master’s and bachelor’s programs serve as significant outlets for the findings of the research group, fostering a dynamic relationship between research and education.

