Review of clothing disposal reasons
Authors: Kirsi Laitala and Ingun Grimstad Klepp, SIFO
Abstract
Garment lifetimes and longer serviceable life play important roles in discussions about the sustainability of clothing consumption.
A compilation of the research on clothing disposal motivations shows that there are three main reasons for disposal:
- Intrinsic quality (37%): Wear and tear-related issues such as shrinkage, tears and holes, fading of colour, broken zippers and loss of technical functions such as waterproofness.
- Fit (28%): Garments that do not fit either because the user has changed size, or the garment did not fit well to start with (for example due to unsuitable grading, insufficient wear ease or wrong size).
- Perceived value (35%): reasons where the consumer no longer wants the garment because it is outdated or out of fashion, or no longer is needed or wanted, or is not valued, for example when there is a lack of space in the wardrobe.
This shows that almost two-thirds of garments are discarded for reasons other than physical durability. Poor fit/design together with lack of perceived value by the owner are responsible for the majority of clothing disposals.
Physical strength is one of the several factors that are important if the lifetime of clothing is to be increased. However, it does not help to make clothes stronger if they are not going to be used longer anyway; this will just contribute to increased environmental impacts from the production and disposal phases. We do not need disposable products» that last for centuries. To work with reducing the environmental impacts of clothing consumption, it is important to optimize the match between strength, value and fit. This has the potential to reduce overproduction. Optimizing clothing lifespans will ensure the best possible utilization of the materials in line with the intentions of the circular economy.
Introduction
Garment lifetimes and longer serviceable life play important roles in discussions about the sustainability of clothing consumption.
Here we present the empirical findings summarized from the research that exists around clothing disposal. The review was originally conducted for the work with the development of durability criteria for Product Environmental Footprint Category Rules (PEFCR) for apparel and footwear. We believe this can be useful information for companies working to improve their products, and debate about clothing sustainability including the understanding of PEF.
We would like to thank Roy Kettlewell and Angus Ireland for their cooperation.
Method
The review includes empirical quantitative studies on clothing disposal reasons. The studies use varying methods, where online surveys are the most commonly used, but also two physical wardrobe studies are included. The way disposal reasons are studied varies as well. Many surveys ask for general, most common disposal reasons, while wardrobe studies and a few of the surveys focus on specific garments that the informants have disposed of. One of the online wardrobe surveys also asks for anticipated disposal reasons for specific garments instead of past behavior. All of the studies have been conducted between 1987 and 2020. The review excluded any studies that did not focus on disposal reasons or did not report results in a quantitative manner. In addition, it excludes a few lower-quality studies with methodological issues. In total 17 studies that fulfil the inclusion criteria were found.
Results
The review shows that clothing is discarded for many reasons. Table 1 summarizes the results and gives some information about the study sample such as where it was conducted and the number of respondents, as well as the main method that was used. Although there are differences between the surveys, they show a common feature. The results on disposal reasons could be placed in three main categories that were found in all reviewed studies: 1) intrinsic quality, 2) fit, and 3) perceived value, and an additional category for 4) other or unknown reasons. The categories include the following disposal reasons:
- Intrinsic quality: Wear and tear-related issues such as shrinkage, tears and holes, fading of colour, broken zippers and loss of technical functions such as waterproofness.
- Fit: Garments that do not fit either because the user has changed size, or the garment did not fit well to start with (for example due to unsuitable grading, insufficient wear ease or wrong size).
- Perceived value: reasons where the consumer no longer wants the garment because it is outdated or out of fashion, or no longer is needed or wanted, or is not valued, for example when there is a lack of space in the wardrobe.
| Study | Research design and sample size | Intrinsic quality | Fit | Perceived value | Other / unknown |
| AC Nielsen (Laitala & Klepp, 2020) | Survey in five countries, 1111 adults aged 18-64, anticipated disposal reason of 40,356 garments | 44 | 13 | 35 | 9 |
| WRAP (2017) | Survey in the UK, 2058 adults, 16,895 garments, disposal reasons per clothing category past year | 18 | 42 | 33 | 7 |
| Laitala, Boks, and Klepp (2015) | Wardrobe study in Norway, 25 adults (9 men and 16 women), 396 discarded garments | 50 | 16 | 24 | 10 |
| Klepp (2001) | Wardrobe study in Norway, 24 women aged 34- 46. 329 discarded garments | 31 | 15 | 33 | 21 |
| Collett, Cluver, and Chen (2013) | Interviews in the USA, 13 female students (aged 18 – 28). Each participant brought five fast fashion items that they no longer wear | 41 | 38 | 21 | – |
| Chun (1987) | Survey in the USA, 89 female students (aged 18 – 30). Most recent garment disposal reason. | 6 | 29 | 56 | 9 |
| Lang, Armstrong, and Brannon (2013) | Survey in the USA, 555 adults. General garment disposal reasons. | 30 | 31 | 39 | – |
| Koch and Domina (1997) | Survey in the USA, 277 students (82% female). General disposal reasons and methods. | 29 | 38 | 33 | – |
| Koch and Domina (1999) and Domina and Koch (1999) | Survey in the USA, 396 adults (88% female). General disposal reasons and methods. | 21 | 37 | 42 | – |
| Zhang et al. (2020) | Survey in China, 507 adults (53% female). General disposal reasons. | 43 | 19 | 22 | 16 |
| Ungerth and Carlsson (2011) | Survey in Sweden, 1014 adults (age 16 – 74). The most common disposal reason. | 60 | 8 | 21 | 9 |
| YouGov (Stevanin, 2019) | Survey in Italy, 992 adults, general disposal reasons. | 31 | 24 | 20 | 25 |
| YouGov (2017a, 2017b, 2017c, 2017d, 2017e) | Surveys in Australia, Philippine, Malaysia, Hong Kong & Singapore, in total 12,434 adults. General disposal reasons. | 39 | 25 | 29 | 7 |
| Mean | Approx. 20,000 adults | 34.1 | 25.8 | 31.4 | 12.6 |
When the category of other/unknown reasons is excluded, the division between the three main disposal reason categories is quite similar, with intrinsic quality constituting about 37% of disposal reasons, followed by lack of perceived value (35%) and poor fit (28%) (Figure 1).
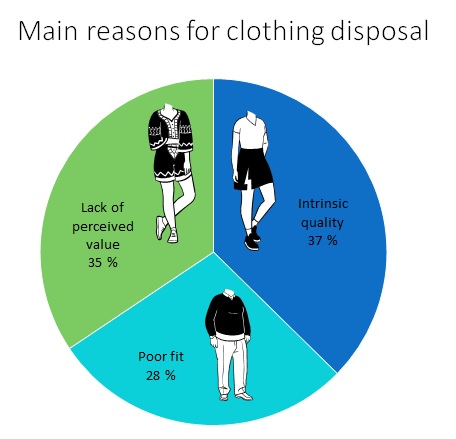
Conclusion
A compilation of the research on clothing disposal motivations shows that there are three main reasons for disposal. Intrinsic quality, that is wear and tear and other physical changes of garments is the dominating disposal reason (37%), followed by lack of perceived value (35%) and poor fit (28%). This shows that almost two-thirds of garments are discarded for reasons other than physical durability. Poor fit/design together with lack of perceived value by the owner are responsible for the majority of clothing disposals.
Physical strength is one of the several factors that are important if the lifetime of clothing is to be increased. However, it does not help to make clothes stronger if they are not going to be used longer anyway: this will just contribute to increased environmental impacts from the production and disposal phases. We do not need «disposable products» that last for centuries. To work with reducing the environmental impacts of clothing consumption, it is important to optimize the match between strength, value and fit. Optimizing clothing lifespans will ensure the best possible utilization of the materials in line with the intentions of the circular economy.
References
Chun, H.-K. (1987). Differences between fashion innovators and non-fashion innovators in their clothing disposal practices. (Master’s thesis). Oregon State University, Corvallis. https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/concern/graduate_thesis_or_dissertations/v118rk195
Collett, M., Cluver, B., & Chen, H.-L. (2013). Consumer Perceptions the Limited Lifespan of Fast Fashion Apparel. Research Journal of Textile and Apparel, 17(2), 61-68. doi:10.1108/RJTA-17-02-2013-B009
Domina, T., & Koch, K. (1999). Consumer reuse and recycling of post-consumer textile waste. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 3(4), 346 – 359. doi:10.1108/eb022571
Klepp, I. G. (2001). Hvorfor går klær ut av bruk? Avhending sett i forhold til kvinners klesvaner [Why are clothes no longer used? Clothes disposal in relationship to women’s clothing habits]. Retrieved from Oslo: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12199/5390
Koch, K., & Domina, T. (1997). The effects of environmental attitude and fashion opinion leadership on textile recycling in the US. Journal of Consumer Studies & Home Economics, 21(1), 1-17. doi:10.1111/j.1470-6431.1997.tb00265.x
Koch, K., & Domina, T. (1999). Consumer Textile Recycling as a Means of Solid Waste Reduction. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal, 28(1), 3-17. doi:10.1177/1077727×99281001
Laitala, K., Boks, C., & Klepp, I. G. (2015). Making Clothing Last: A Design Approach for Reducing the Environmental Impacts. International Journal of Design, 9(2), 93-107.
Laitala, K., & Klepp, I. G. (2020). What Affects Garment Lifespans? International Clothing Practices Based on a Wardrobe Survey in China, Germany, Japan, the UK, and the USA. Sustainability, 12(21), 9151. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/21/9151
Lang, C., Armstrong, C. M., & Brannon, L. A. (2013). Drivers of clothing disposal in the US: An exploration of the role of personal attributes and behaviours in frequent disposal. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 37(6), 706-714. doi:10.1111/ijcs.12060
Stevanin, E. (2019). Fast fashion: il continuo rinnovo del guardaroba. Retrieved from https://it.yougov.com/news/2019/05/27/fast-fashion-il-rinnovo-del-guardaroba/
Ungerth, L., & Carlsson, A. (2011). Vad händer sen med våra kläder? Enkätundersökning. Stockholm: http://www.konsumentforeningenstockholm.se/Global/Konsument%20och%20Milj%c3%b6/Rapporter/KfS%20rapport_april11_Vad%20h%c3%a4nder%20sen%20med%20v%c3%a5ra%20kl%c3%a4der.pdf
WRAP. (2017). Valuing Our Clothes: the cost of UK fashion. http://www.wrap.org.uk/sites/files/wrap/valuing-our-clothes-the-cost-of-uk-fashion_WRAP.pdf
YouGov. (2017a). Fast fashion: 27% of Malaysians have thrown away clothing after wearing it just once. Retrieved from https://my.yougov.com/en-my/news/2017/12/06/fast-fashion/
YouGov. (2017b). Fast fashion: 39% of Hong Kongers have thrown away clothing after wearing it just once. Retrieved from https://hk.yougov.com/en-hk/news/2017/12/06/fast-fashion/
YouGov. (2017c). Fast fashion: a third of Filipinos have thrown away clothing after wearing it just once. Retrieved from https://ph.yougov.com/en-ph/news/2017/12/06/fast-fashion/
YouGov. (2017d). Fast fashion: a third of Singaporeans have thrown away clothing after wearing it just once. Retrieved from https://sg.yougov.com/en-sg/news/2017/12/06/fast-fashion/
YouGov. (2017e). Fast fashion: Three in ten Aussies have thrown away clothing after wearing it just once. Retrieved from www.au.yougov.com/news/2017/12/06/fast-fashion/
Zhang, L., Wu, T., Liu, S., Jiang, S., Wu, H., & Yang, J. (2020). Consumers’ clothing disposal behaviors in Nanjing, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 276, 123184.


